Unlocking the Secrets of Emollients: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Hydration and Repair
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Emollients: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Hydration and Repair
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Emollients: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Hydration and Repair. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Emollients: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Hydration and Repair
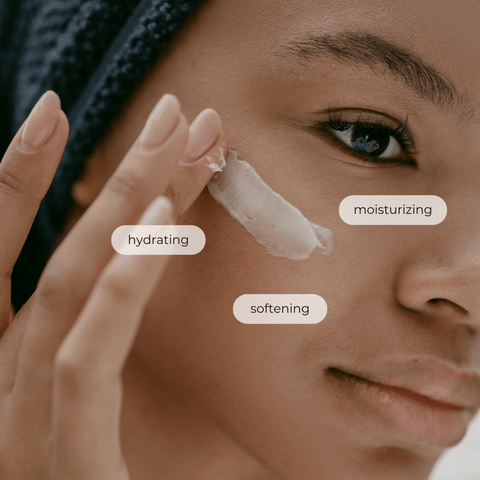

Emollients, the unsung heroes of skincare, play a crucial role in maintaining healthy, supple skin. These moisturizing agents work by replenishing and retaining moisture, addressing dryness and restoring the skin’s protective barrier. Understanding the diverse world of emollients empowers informed skincare choices, enabling individuals to select the most suitable products for their unique needs.
A Deep Dive into the World of Emollients
Emollients are broadly classified into two main categories: occlusives and humectants. Each category employs distinct mechanisms to achieve optimal hydration, offering a tailored approach to skin care.
1. Occlusives: The Barrier Builders
Occlusives form a protective layer on the skin’s surface, preventing moisture loss and promoting hydration. They act as a shield, trapping existing moisture within the skin and minimizing water evaporation. This mechanism is particularly beneficial for individuals with severely dry skin, eczema, or other conditions that compromise the skin’s natural barrier.
a) Petroleum-Based Occlusives:
- Mineral Oil: This widely available and affordable ingredient is highly effective in sealing in moisture. While non-comedogenic (does not clog pores), it can leave a greasy residue, making it unsuitable for oily skin.
- Petrolatum: This thick, semi-solid petroleum product is a highly effective occlusive, renowned for its ability to heal chapped skin and protect against environmental damage.
- Paraffin: A waxy substance derived from petroleum, paraffin is another effective occlusive, often found in lip balms and hand creams.
b) Plant-Derived Occlusives:
- Lanolin: Derived from sheep’s wool, lanolin is a natural occlusive with excellent moisturizing properties. It is particularly beneficial for dry, sensitive skin, but some individuals may experience allergic reactions.
- Shea Butter: This rich, creamy butter extracted from the shea tree is a potent occlusive, known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It is a popular choice for addressing dry skin, eczema, and stretch marks.
- Cocoa Butter: A rich source of fatty acids and antioxidants, cocoa butter is a gentle occlusive, suitable for sensitive skin. It is often used in lip balms and moisturizers.
c) Synthetic Occlusives:
- Dimethicone: A silicone-based ingredient, dimethicone is a lightweight occlusive that provides a smooth, non-greasy finish. It is commonly found in anti-aging products and sunscreens.
- Cyclomethicone: A volatile silicone, cyclomethicone evaporates quickly, leaving a smooth, silky feel. It is often used in hair care products and makeup.
2. Humectants: The Moisture Magnets
Humectants work by attracting and drawing moisture from the air to the skin’s surface. They act like sponges, absorbing water molecules and replenishing the skin’s natural moisture content. Humectants are particularly effective in humid environments, where they can readily absorb moisture from the air.
a) Natural Humectants:
- Glycerin: A highly effective humectant, glycerin is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol that attracts and retains moisture. It is widely used in skincare products for its hydrating and soothing properties.
- Hyaluronic Acid: This powerful humectant can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, making it an exceptional hydrating agent. It is particularly effective for dry, dehydrated skin and is often used in anti-aging products.
- Honey: A natural humectant with antibacterial and antioxidant properties, honey is a gentle moisturizer that soothes and nourishes the skin.
b) Synthetic Humectants:
- Sodium PCA: A naturally occurring amino acid, sodium PCA is a powerful humectant that effectively draws moisture to the skin. It is often found in moisturizers and serums.
- Propylene Glycol: A synthetic humectant, propylene glycol is a highly effective moisture-attracting agent. It is often used in skincare products and cosmetics.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Benefits of Emollients
Emollients offer a multitude of benefits for the skin, beyond simply providing hydration. Their unique properties address various skin concerns, contributing to overall skin health and vitality.
1. Restoring the Skin’s Protective Barrier:
Emollients play a crucial role in restoring the skin’s natural barrier function, which is essential for protecting the skin from external aggressors like bacteria, viruses, and irritants. This barrier, composed of lipids and proteins, prevents moisture loss and maintains the skin’s integrity.
2. Alleviating Dryness and Itchiness:
Dryness and itchiness are common symptoms of compromised skin barrier function. Emollients effectively address these concerns by restoring moisture levels and reducing inflammation, providing much-needed relief.
3. Promoting Skin Cell Regeneration:
Emollients can stimulate skin cell regeneration, contributing to a youthful and healthy complexion. They accelerate the process of replacing damaged skin cells with new, healthy ones, promoting a smoother and more even skin tone.
4. Minimizing the Appearance of Fine Lines and Wrinkles:
Emollients can improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by hydrating the skin and plumping it up. This effect helps to smooth out the skin’s surface and create a more youthful appearance.
5. Reducing Inflammation and Redness:
Emollients can help reduce inflammation and redness associated with various skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea. Their soothing and anti-inflammatory properties provide relief and promote healing.
FAQs by Different Types of Emollients and Their Uses
1. Occlusives
Q: What are the best occlusives for dry skin?
A: Petroleum-based occlusives like mineral oil and petrolatum are highly effective for severely dry skin. Plant-derived occlusives like shea butter and cocoa butter are also excellent options, offering additional benefits like antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties.
Q: Can occlusives cause breakouts?
A: While some occlusives can clog pores, leading to breakouts, others are non-comedogenic. Mineral oil, petrolatum, and dimethicone are generally considered non-comedogenic, while lanolin can be pore-clogging for some individuals.
Q: How often should I apply occlusives?
A: The frequency of application depends on the severity of dryness. For severely dry skin, applying occlusives twice daily may be necessary, while those with milder dryness can use them once a day or as needed.
2. Humectants
Q: Are humectants suitable for all skin types?
A: Humectants are generally suitable for all skin types, including oily skin. They can help to balance moisture levels and prevent excessive oil production.
Q: How do humectants work in humid environments?
A: Humectants are particularly effective in humid environments, where they can readily absorb moisture from the air. This makes them ideal for maintaining skin hydration in climates with high humidity.
Q: Can humectants cause dryness?
A: While humectants attract moisture, they can also draw moisture from the deeper layers of the skin if the air is dry. To prevent this, it is essential to follow up with an occlusive to lock in the moisture.
Tips by Different Types of Emollients and Their Uses
1. Occlusives
- Choose the right occlusive for your skin type: Consider your skin’s sensitivity, oiliness, and specific concerns.
- Apply occlusives to damp skin: This allows the occlusive to trap moisture more effectively.
- Layer occlusives with humectants: Combining an occlusive with a humectant provides optimal hydration and prevents moisture loss.
2. Humectants
- Use humectants in the morning and evening: This helps to maintain consistent hydration throughout the day.
- Apply humectants to damp skin: This allows them to absorb moisture more effectively.
- Pair humectants with a moisturizer: This helps to seal in moisture and prevent evaporation.
Conclusion by Different Types of Emollients and Their Uses
Emollients are essential components of a comprehensive skincare routine, providing hydration, protection, and repair for the skin. Understanding the diverse world of emollients, their mechanisms of action, and their unique benefits empowers informed skincare choices. By selecting the right emollients for individual needs, individuals can unlock the secrets to healthy, radiant, and youthful skin.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cerave-6b9f7943e28e4664bb0c6d3fa16ced43.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/no7-c0a79c4ba4cc48f98dc20a3c171cd04d.jpeg)

/USED_Emollients-for-Skin-4108-1x1-hires-6733ccb3fa0c4bda8af234dda2f1a1b3.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Emollients: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Hydration and Repair. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!