The Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide

The human skin, our largest organ, serves as a vital barrier, protecting us from the external environment while regulating temperature and enabling sensory perception. Maintaining optimal skin health is crucial for overall well-being, impacting both physical and mental aspects of our lives. This comprehensive guide delves into the science of skin health, exploring its intricate structure, common concerns, and effective strategies for achieving and preserving healthy skin.
Understanding the Structure and Function of Skin
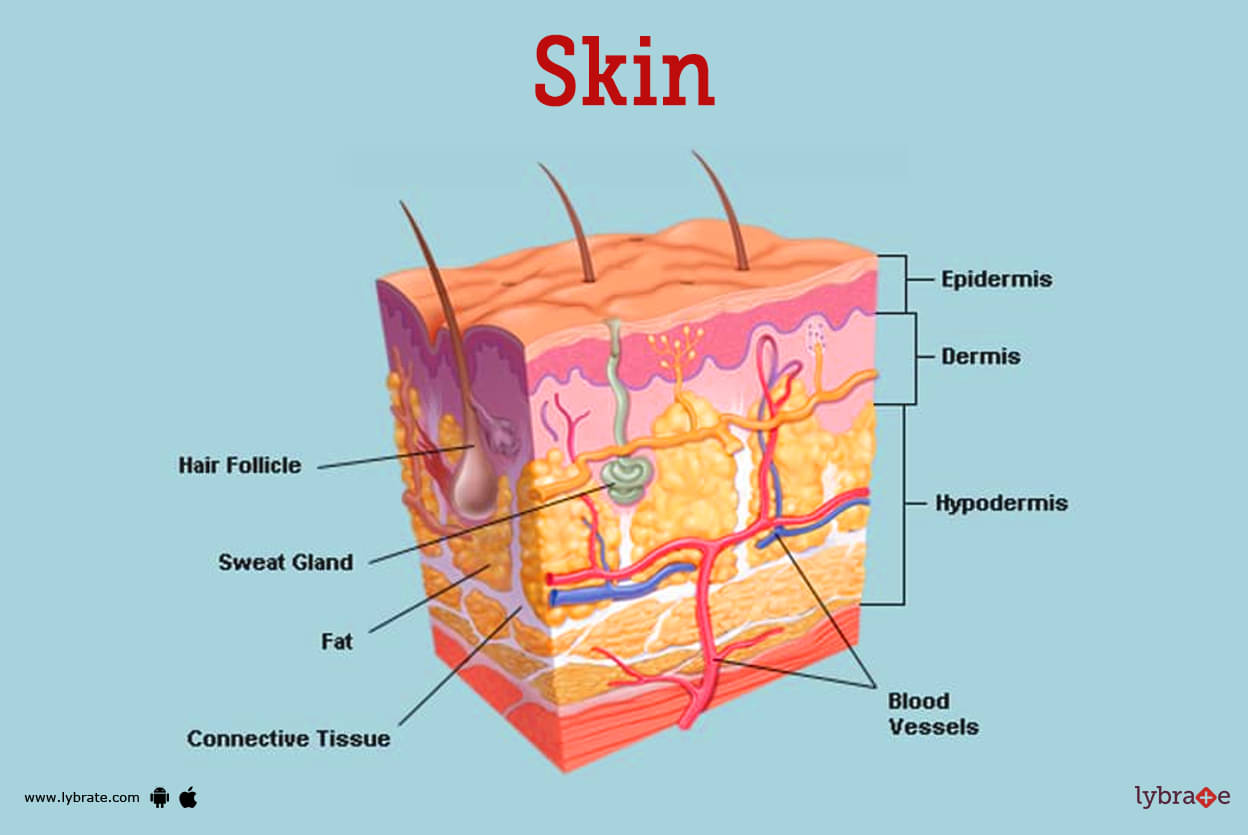
The skin comprises three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer. Each layer plays a specific role in maintaining skin health:
-
Epidermis: The outermost layer, responsible for protecting the body from external elements. It contains keratinocytes, which produce keratin, a protein that provides structural support and forms a protective barrier. Melanocytes, responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and protects it from UV radiation, reside in the epidermis.
-
Dermis: Located beneath the epidermis, the dermis houses blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It also contains collagen and elastin fibers, providing the skin with its elasticity and strength.
-
Subcutaneous Layer: The deepest layer, composed primarily of fat cells, provides insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. It also contains blood vessels and nerves, connecting the skin to the underlying tissues.
Common Skin Concerns and Their Causes
While the skin serves as a protective shield, it is susceptible to various factors that can compromise its health. Common skin concerns include:
-
Acne: Characterized by inflamed pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, acne develops due to clogged hair follicles, often exacerbated by hormonal fluctuations, bacteria, and excess oil production.
-
Eczema: A chronic condition characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed skin patches, eczema is often triggered by allergens, irritants, or genetic predisposition.
-
Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune disease causing red, scaly patches on the skin, psoriasis results from an overproduction of skin cells, leading to thickened, inflamed areas.
-
Rosacea: A common skin condition causing redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the face, rosacea is often triggered by environmental factors, such as sun exposure, stress, and alcohol consumption.
-
Skin Cancer: A serious condition characterized by abnormal cell growth in the skin, skin cancer can be caused by excessive sun exposure, genetic predisposition, and certain environmental factors.
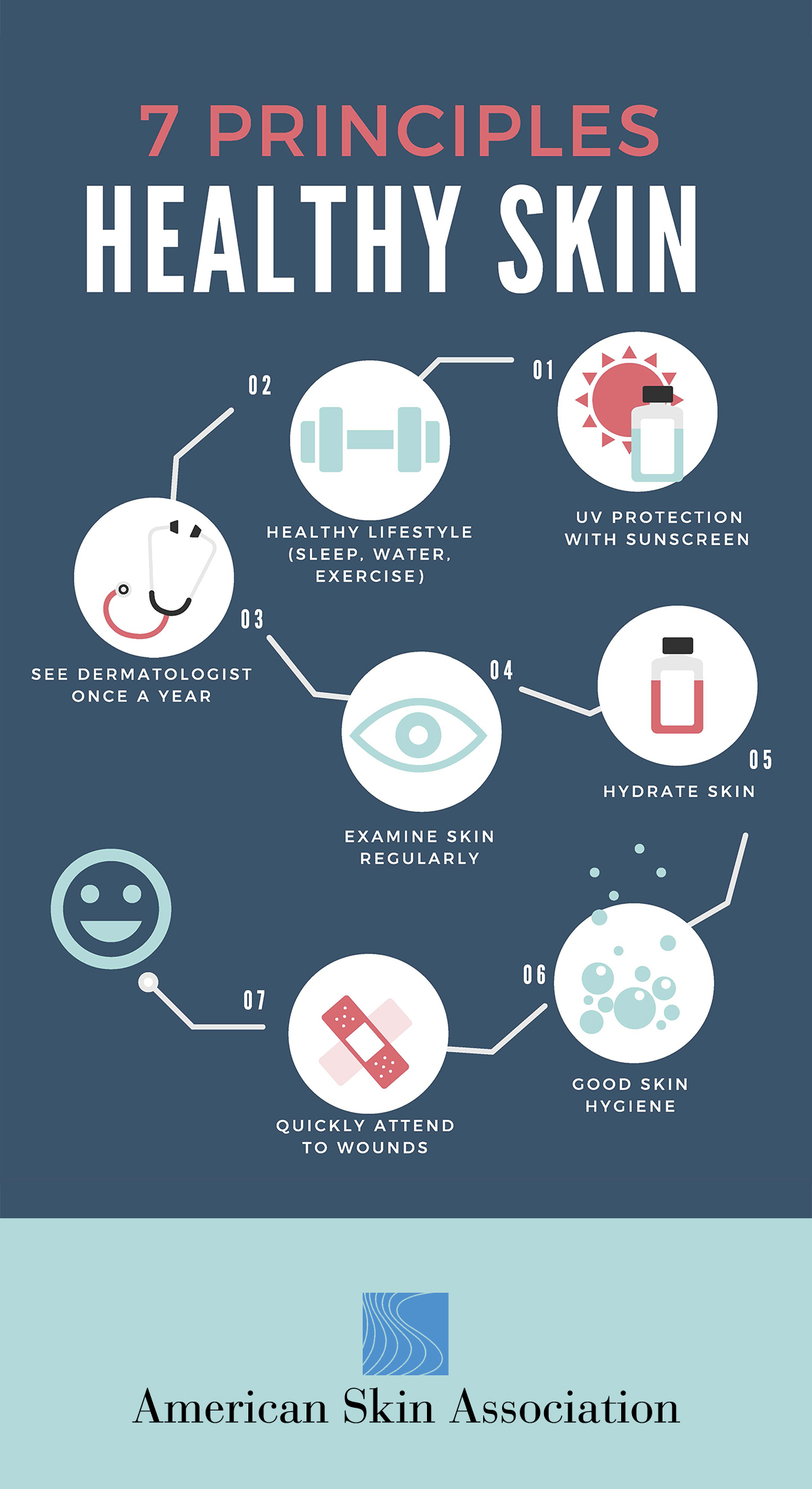
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Skin
Maintaining healthy skin involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing lifestyle modifications, skincare practices, and medical interventions:
-
Sun Protection: Limiting sun exposure and using sunscreen with a high SPF are crucial for preventing sun damage and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
-
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and using moisturizers help maintain skin hydration, preventing dryness and promoting elasticity.
-
Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants supports skin health by providing essential nutrients for skin cell regeneration and protection.
-
Cleanliness: Regularly cleansing the skin removes dirt, oil, and pollutants, preventing clogged pores and reducing the risk of breakouts.
-
Exfoliation: Gently exfoliating the skin removes dead cells, promoting cell turnover and improving skin texture.
-
Stress Management: Stress can negatively impact skin health, leading to breakouts and inflammation. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and mindfulness can improve skin condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the best way to prevent wrinkles?
A: While aging is a natural process, several factors contribute to wrinkle formation, including sun exposure, smoking, and genetics. Maintaining adequate hydration, using sunscreen consistently, and incorporating anti-aging products into your skincare routine can help minimize wrinkle formation.
Q: How often should I exfoliate my skin?
A: The frequency of exfoliation depends on your skin type and individual needs. Generally, exfoliating 1-2 times per week is sufficient for most individuals, while those with sensitive skin may benefit from exfoliating less frequently.
Q: Can I use any type of soap on my face?
A: Facial skin is delicate and requires gentle cleansing. Harsh soaps can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Opt for mild, pH-balanced cleansers specifically designed for facial use.
Q: What are the signs of skin cancer?
A: Skin cancer can manifest in various ways, but common signs include:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole or lesion does not match the other half.
- Border irregularity: The edges are uneven, notched, or blurred.
- Color variation: The color is uneven, with shades of brown, black, red, or white.
- Diameter larger than 6 millimeters: The mole or lesion is larger than a pencil eraser.
- Evolving: The mole or lesion changes in size, shape, or color.
If you notice any of these signs, consult a dermatologist immediately.
Tips for Healthy Skin
- Use a gentle cleanser: Avoid harsh soaps and detergents that can strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Moisturize regularly: Apply moisturizer to damp skin after cleansing to lock in hydration.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Eat a balanced diet: Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet to provide essential nutrients for skin health.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger breakouts and inflammation. Practice relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, to manage stress levels.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for cell regeneration and repair. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- See a dermatologist regularly: Regular checkups can help detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy skin is an ongoing journey that requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, skincare practices, and medical interventions. By understanding the structure and function of the skin, common concerns, and effective strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to achieve and preserve optimal skin health, contributing to overall well-being. Remember, the skin is our largest organ and deserves the attention and care it needs to thrive.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!