The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
Related Articles: The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
- 3.1 The Nutritional Powerhouse Within the Skin
- 3.2 Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
- 3.3 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Plum Skin
- 3.4 Tips for Incorporating Plum Skin into Your Diet
- 3.5 Conclusion: Embracing the Nutritional Power of Plum Skin
- 4 Closure
The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
Plums, with their vibrant hues and juicy sweetness, are a beloved fruit enjoyed worldwide. While many relish the succulent flesh, the fate of the skin often remains a point of contention. Some discard it without a second thought, while others might wonder about its edibility and potential benefits. This article delves into the nutritional value and culinary uses of plum skin, providing a comprehensive understanding of its role in the world of plums.
The Nutritional Powerhouse Within the Skin
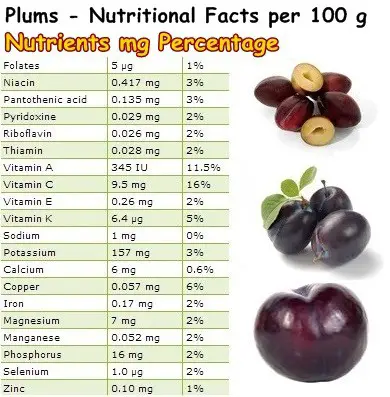
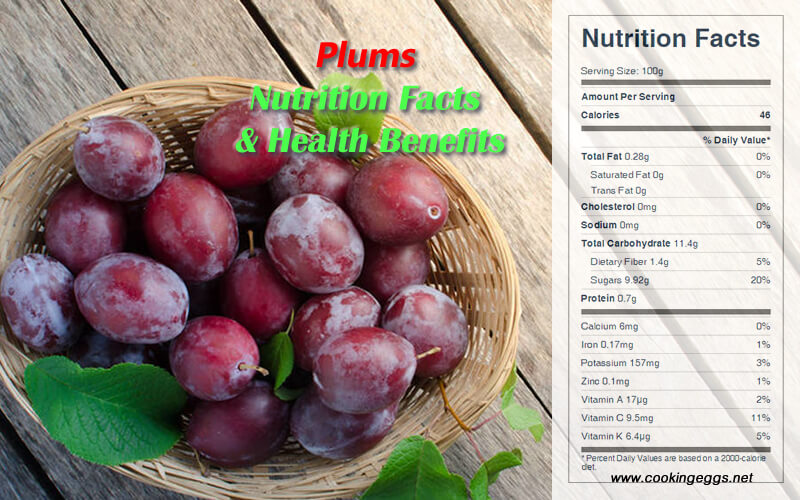
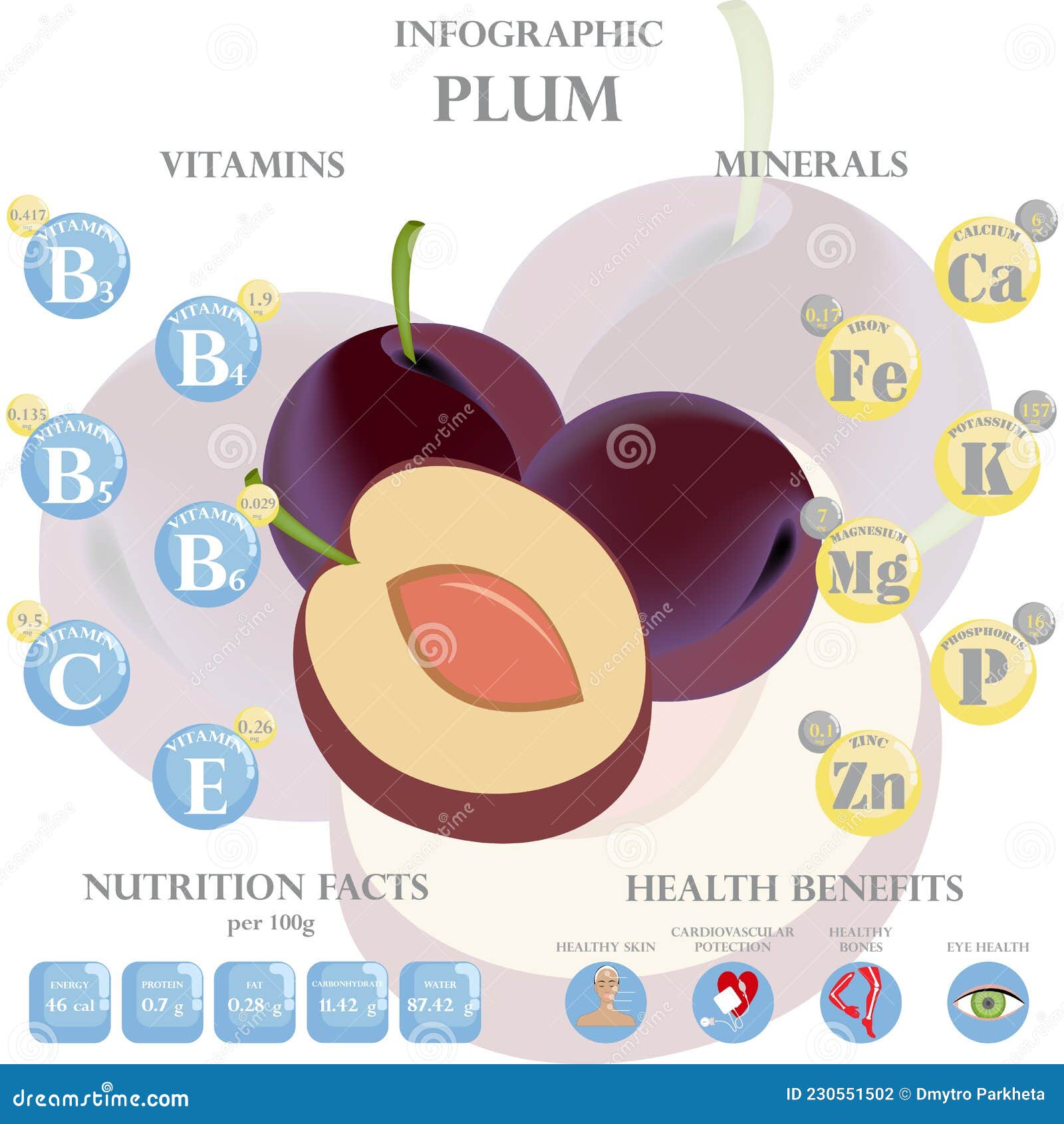
Contrary to popular belief, plum skin is not merely a protective layer; it is a treasure trove of nutrients. Packed with fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins, plum skin offers a range of health benefits that shouldn’t be overlooked.
Fiber: Plum skin is an excellent source of dietary fiber, particularly insoluble fiber. This type of fiber adds bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. It also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels, reducing cholesterol, and contributing to a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management.
Antioxidants: Plum skin boasts a rich concentration of antioxidants, such as polyphenols and flavonoids. These compounds combat free radicals, which are unstable molecules that damage cells and contribute to aging and chronic diseases. Antioxidants in plum skin have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative conditions.
Vitamin C: Plum skin is a good source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant essential for immune function, collagen production, and wound healing. Vitamin C also aids in iron absorption and contributes to healthy skin, hair, and bones.
Other Nutrients: Plum skin also contains other beneficial nutrients, including vitamin K, potassium, and manganese. Vitamin K is crucial for blood clotting and bone health, while potassium regulates blood pressure and muscle function. Manganese is a cofactor for various enzymes involved in metabolism and antioxidant defense.
Culinary Uses of Plum Skin
The nutritional value of plum skin extends beyond its health benefits; it also adds a unique dimension to culinary creations.
Preserves and Jams: Plum skin contributes a vibrant color and a subtle bitterness to homemade preserves and jams, enhancing their flavor profile and adding a touch of complexity. When simmered with sugar and fruit, the skin softens and releases its natural pectin, creating a thicker, more satisfying texture.
Dried Plums: Dried plums, or prunes, are often made with the skin intact. The skin adds a chewy texture and a concentrated sweetness to the dried fruit. It also contributes to the high fiber content of prunes, making them a popular choice for digestive health.
Plum Skin Tea: Plum skin can be used to create a flavorful and healthy tea. Simply simmer dried plum skin in water for several minutes, then strain and enjoy. Plum skin tea is believed to have digestive benefits and may also help to reduce inflammation.
Infused Oils and Vinegars: Plum skin can be infused into oils and vinegars to create unique flavors and aromas. The skin imparts a subtle fruity sweetness and a hint of bitterness, adding a complex dimension to dressings, marinades, and sauces.
Other Culinary Uses: Plum skin can be incorporated into various recipes, adding texture and flavor. It can be finely chopped and added to salads, salsas, or chutneys. It can also be used as a natural food coloring agent, adding a vibrant hue to baked goods and desserts.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Plum Skin
1. Is it safe to eat plum skin?
Yes, plum skin is perfectly safe to eat. It is a natural part of the fruit and contains valuable nutrients. However, it is important to wash the plums thoroughly before consuming them, including the skin, to remove any dirt or pesticides.
2. Does plum skin taste bitter?
Plum skin can have a slightly bitter taste, especially in some varieties. The bitterness is due to the presence of tannins, which are also responsible for the skin’s vibrant color. However, the bitterness is often subtle and can be balanced by the sweetness of the fruit.
3. Can I eat plum skin if I have digestive issues?
While plum skin is high in fiber, which can benefit digestion, individuals with sensitive digestive systems may experience discomfort when consuming it. If you have a history of digestive issues, it is advisable to start with small amounts of plum skin and gradually increase your intake as tolerated.
4. Are there any health risks associated with eating plum skin?
There are no known health risks associated with eating plum skin. However, some individuals may be allergic to plums, and consuming the skin could trigger an allergic reaction. If you have a known plum allergy, it is best to avoid eating the skin.
5. Can I eat the skin of all plum varieties?
Yes, you can generally eat the skin of all plum varieties. However, some varieties may have thicker or tougher skins, which can be more challenging to chew. If you find the skin difficult to eat, you can always remove it before consuming the fruit.
Tips for Incorporating Plum Skin into Your Diet
1. Wash and Scrub: Always wash plums thoroughly before eating them, including the skin. Use a vegetable brush to scrub away any dirt or residue.
2. Start Slowly: If you are new to eating plum skin, start with small amounts and gradually increase your intake as tolerated.
3. Choose Ripe Plums: Ripe plums have softer skins, which are easier to chew and digest. Avoid consuming unripe plums, as their skins can be tough and bitter.
4. Experiment with Recipes: Explore different recipes that incorporate plum skin, such as jams, preserves, and teas.
5. Be Mindful of Allergies: If you have a known plum allergy, avoid eating the skin.
Conclusion: Embracing the Nutritional Power of Plum Skin
The next time you savor a juicy plum, consider embracing the nutritional wealth of its skin. From fiber to antioxidants, plum skin offers a range of health benefits that contribute to overall well-being. By incorporating plum skin into your diet, you can enjoy the full nutritional potential of this delightful fruit, adding a touch of flavor and a boost of health to your culinary adventures.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plum_annotated-4c30abcb0ed54a6aae56464fff498262.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nutritional Value and Culinary Uses of Plum Skin. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!