The Complex Relationship Between Skincare and Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Solutions
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Skincare and Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Solutions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Skincare and Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Solutions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between Skincare and Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Solutions

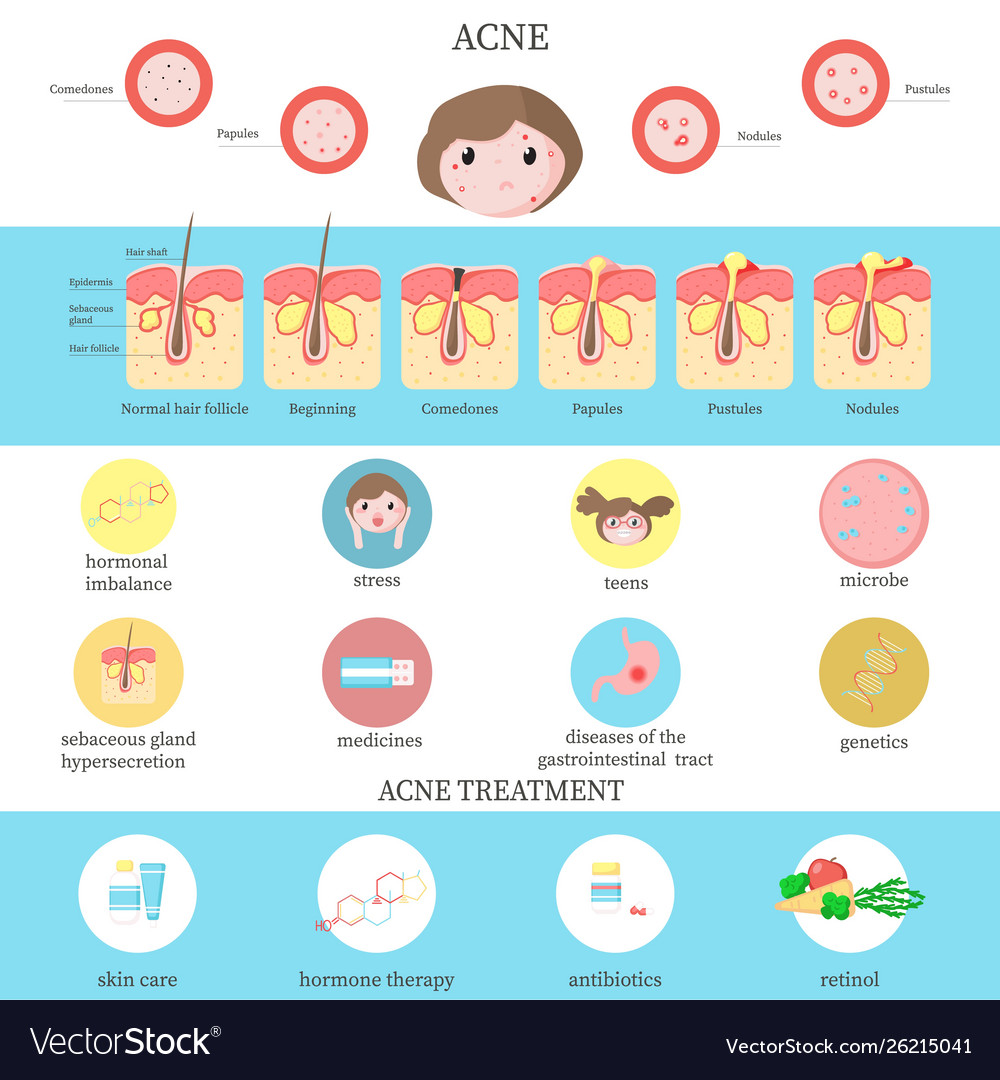
Acne, a common skin condition characterized by blemishes, pimples, and cysts, affects millions worldwide. While hormonal fluctuations and genetics play a significant role in its development, the products we apply to our skin can also influence its severity and appearance. This article delves into the intricate relationship between skincare and acne, exploring the potential triggers, preventative measures, and strategies for managing this prevalent skin concern.
Understanding Acne: A Multifaceted Condition
Acne arises from a combination of factors, including:
- Excess sebum production: Sebum, an oily substance produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands, can clog pores when overproduced.
- Hyperkeratinization: This refers to the excessive build-up of dead skin cells within the hair follicles, further obstructing the pores.
- Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes): This bacterium, naturally present on the skin, thrives in clogged pores and contributes to inflammation.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Androgens, hormones primarily associated with males, can stimulate sebum production, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy.
- Genetics: A predisposition to acne can be inherited, making some individuals more susceptible than others.
Skincare Products: Potential Triggers and Solutions
While many skincare products aim to improve skin health, some ingredients or formulations can inadvertently exacerbate acne. Understanding these potential triggers and choosing products carefully is crucial.
1. Comedogenic Ingredients:
Comedogenic ingredients are known to clog pores, increasing the likelihood of breakouts. These include:
- Oils: Certain oils, like coconut oil, olive oil, and mineral oil, can be comedogenic for some individuals.
- Waxes: Waxes, like beeswax and lanolin, can also contribute to pore blockage.
- Heavy moisturizers: Thick, occlusive moisturizers can trap sebum and debris, promoting acne.
- Silicones: While not inherently comedogenic, silicones can create a barrier on the skin, potentially trapping sebum and contributing to breakouts.
2. Irritating Ingredients:
Some ingredients, while not directly pore-clogging, can irritate the skin and trigger inflammation, exacerbating acne. These include:
- Fragrances: Synthetic fragrances are often a source of irritation, leading to redness, dryness, and increased acne.
- Alcohol: Denatured alcohol, commonly found in toners and astringents, can dry out the skin, leading to increased oil production and inflammation.
- Essential oils: While some essential oils have purported skin benefits, they can also be irritating, particularly for sensitive skin.
- Harsh scrubs: Exfoliating is essential, but using abrasive scrubs can damage the skin barrier, increasing inflammation and acne.
3. Over-exfoliation:
While exfoliation removes dead skin cells and helps prevent clogged pores, over-exfoliating can damage the skin barrier, leaving it vulnerable to bacteria and inflammation, potentially worsening acne.
4. Improper Product Application:
Applying too much product, particularly heavy creams or oils, can overload the skin and contribute to clogged pores.
5. Product Sensitivity:
Individual sensitivities to certain ingredients can trigger allergic reactions, leading to redness, itching, and breakouts.
Navigating Skincare for Acne-Prone Skin: A Guide to Safe Practices
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Opt for products labeled "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free," which are less likely to clog pores.
- Minimize Irritants: Avoid products containing harsh fragrances, alcohol, and essential oils, especially if you have sensitive skin.
- Exfoliate Gently: Choose gentle exfoliants, such as chemical exfoliants with alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), and use them sparingly.
- Hydrate Appropriately: Opt for lightweight, oil-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
- Cleanse Twice Daily: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
- Patch Test New Products: Before applying a new product to your entire face, test it on a small area of your skin to check for any reactions.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you have persistent or severe acne, seek professional advice from a dermatologist. They can diagnose the underlying cause and recommend personalized treatment options.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns about Skincare and Acne
Q: Can using makeup worsen acne?
A: Makeup can contribute to acne if it is comedogenic or if it is not removed properly. Choose oil-free, non-comedogenic makeup, and ensure you remove it thoroughly at the end of the day.
Q: Can using sunscreen cause acne?
A: Some sunscreens can be comedogenic, but there are many non-comedogenic options available. Look for sunscreens labeled "oil-free" or "non-comedogenic."
Q: Is it necessary to change my skincare routine when I have acne?
A: Yes, it’s essential to adapt your skincare routine when dealing with acne. Choose products designed for acne-prone skin and avoid ingredients that can irritate or clog pores.
Q: Can using a moisturizer worsen acne?
A: Not necessarily. Using a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer can help keep the skin hydrated, which is important for maintaining a healthy skin barrier and preventing excess oil production.
Q: Can using a face mask worsen acne?
A: Some face masks can be comedogenic or irritating, exacerbating acne. Choose masks specifically designed for acne-prone skin and use them sparingly.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Skin Barrier and Preventing Acne
- Cleanse gently: Avoid harsh cleansers that strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Hydrate regularly: Maintain adequate hydration to support a healthy skin barrier.
- Protect from the sun: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that exacerbate acne.
- Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall skin health.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep allows the skin to repair and regenerate.
Conclusion
While skincare products can play a role in triggering or managing acne, they are not the sole determinant of its severity. Understanding the potential triggers and choosing products carefully is crucial for preventing and managing this common skin concern. By prioritizing gentle cleansing, hydration, sun protection, and avoiding comedogenic and irritating ingredients, individuals can maintain a healthy skin barrier and minimize the risk of acne breakouts. Consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment is recommended for persistent or severe acne.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Skincare and Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Solutions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!