The Art and Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Exploration

The human skin, our largest organ, serves as a protective barrier against the external environment. It is a complex system, constantly adapting and regenerating, requiring careful attention to maintain its health and vitality. This intricate process, encompassing a range of practices and products, is what we refer to as skincare.
Beyond Aesthetics: Unveiling the Importance of Skin Health
While often associated with achieving a youthful appearance or addressing cosmetic concerns, the true significance of skincare extends far beyond superficiality. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding the body’s overall well-being. Healthy skin acts as a formidable defense against:
- Infections: The skin’s outermost layer, the epidermis, serves as a physical barrier, preventing the entry of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Environmental Damage: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollutants, and harsh chemicals can inflict damage to the skin, leading to premature aging, skin cancer, and other dermatological issues.
- Dehydration: The skin plays a vital role in regulating the body’s moisture levels. Maintaining its integrity ensures proper hydration and prevents dryness, itching, and other discomforts.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Skincare
The foundation of effective skincare lies in understanding the fundamental principles that govern its health. These include:
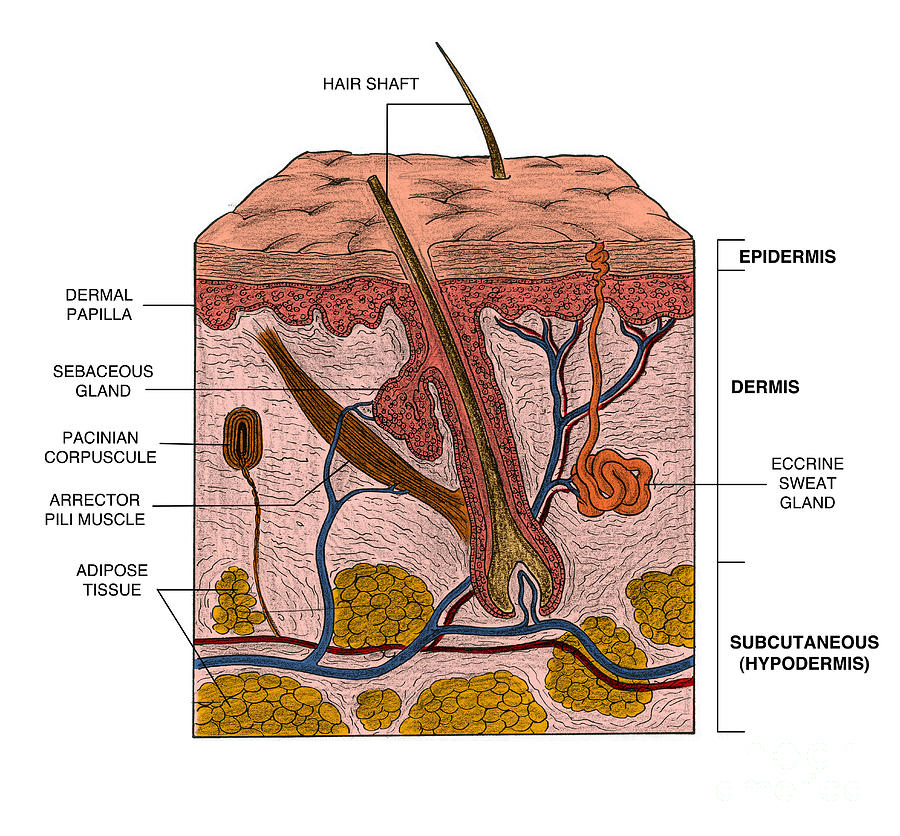
- Skin Structure and Function: The skin comprises three primary layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. Each layer possesses unique characteristics and performs specific functions. Understanding these structures allows for targeted skincare practices.
- Skin Types: Skin types, categorized based on oil production and moisture levels, influence the choice of products and routines. Common skin types include normal, dry, oily, combination, and sensitive.
- Skin Conditions: Various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental influences, can contribute to the development of skin conditions such as acne, eczema, rosacea, and psoriasis. Recognizing these conditions is crucial for appropriate treatment and management.
A Holistic Approach to Skincare
Effective skincare necessitates a comprehensive approach that encompasses:
- Cleansing: Removing dirt, oil, and pollutants accumulated throughout the day is essential for maintaining a healthy skin surface. Choosing the right cleanser based on skin type is paramount.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells, revealing fresh, radiant skin and promoting cell turnover. Physical and chemical exfoliants offer different mechanisms for achieving this goal.
- Moisturization: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for skin health. Moisturizers replenish moisture, improve elasticity, and protect the skin from environmental stressors.
- Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation is essential for preventing premature aging, skin cancer, and other sun-related damage. Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is recommended for daily use.
- Diet and Lifestyle: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants, combined with adequate hydration and healthy lifestyle choices, significantly contributes to healthy skin.
- Professional Care: Consulting with a dermatologist or esthetician can provide personalized advice, diagnose skin conditions, and recommend appropriate treatments.
Navigating the World of Skincare Products
The skincare market is brimming with a plethora of products, each promising to address specific concerns. Understanding the ingredients and their functions is crucial for making informed choices:
- Humectants: These ingredients attract and retain moisture, keeping the skin hydrated. Common examples include hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and aloe vera.
- Emollients: Emollients smooth and soften the skin by filling in gaps between skin cells. Examples include shea butter, cocoa butter, and ceramides.
- Occlusives: Occlusives create a barrier on the skin’s surface, preventing moisture loss. Examples include petroleum jelly, mineral oil, and dimethicone.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, which contribute to aging and other skin issues. Examples include vitamin C, vitamin E, and green tea extract.
- Retinoids: Retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A that promote cell turnover, reduce wrinkles, and improve skin texture. Examples include retinol, retinaldehyde, and tretinoin.
- AHAs and BHAs: Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) are chemical exfoliants that remove dead skin cells and improve skin tone. Examples include glycolic acid, lactic acid, and salicylic acid.
FAQs: Demystifying Common Skincare Questions
Q: What is the best skincare routine for my skin type?
A: The optimal skincare routine varies depending on your individual skin type and concerns. Consulting a dermatologist or esthetician is recommended for personalized advice.
Q: How often should I exfoliate?
A: The frequency of exfoliation depends on your skin type and the type of exfoliant used. Generally, gentle exfoliation 1-2 times a week is sufficient for most individuals.
Q: Is it necessary to use a serum?
A: Serums can be beneficial for addressing specific skin concerns. However, they are not essential for everyone.
Q: How do I choose the right sunscreen?
A: Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and apply liberally to all exposed skin every two hours.
Q: What are the signs of sun damage?
A: Signs of sun damage include wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, uneven skin tone, and skin cancer.
Q: How can I prevent premature aging?
A: Protecting the skin from sun damage, following a healthy diet and lifestyle, and incorporating anti-aging skincare products can help prevent premature aging.
Tips for Effective Skincare
- Consistency is Key: Maintain a consistent skincare routine, even on days when you are not wearing makeup.
- Listen to Your Skin: Pay attention to your skin’s reactions and adjust your routine accordingly.
- Patch Test New Products: Before applying a new product to your entire face, test it on a small area of skin to check for any adverse reactions.
- Use Clean Tools: Ensure that your makeup brushes, sponges, and other tools are clean to prevent bacterial growth and irritation.
- Be Patient: Results from skincare products and routines may take time to become noticeable.
Conclusion: Embracing a Lifetime of Skin Health
Skincare is not merely a cosmetic pursuit; it is an essential aspect of overall health and well-being. By understanding the principles of skin health, adopting a comprehensive approach, and making informed choices about products and practices, individuals can cultivate a healthy and vibrant complexion that lasts a lifetime.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Skin Health: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!